Description
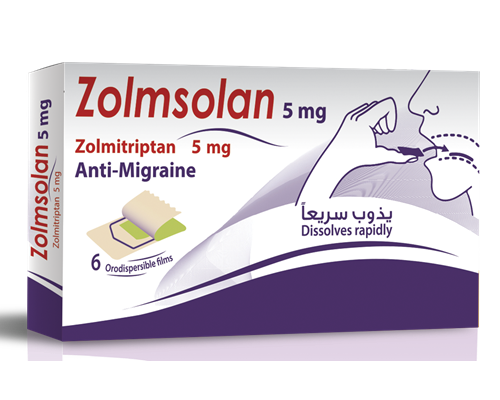
Tradename:
Zolmsolan
Compound:
Each orally soluble film contains:
Zolmitriptan 5 mg
Auxiliary components:
Polyvinyl alcohol, polyethylene glycol, starch, glycerol, sucrose, menthol oil, simethicone.
Properties:
Zolmitriptan is a selective agonist of 5HT1B/1D receptors, the stimulation of which leads to vasoconstriction. It has high affinity for recombinant human 5HT1B/1D receptors and moderate affinity for 5HT1A receptors. Zolmitriptan has no affinity and does not exhibit significant pharmacological activity towards 5HT2-, 5HT3-, 5HT4-, adrenergic, histamine, muscarinic and dopamine receptors.
Administration of zolmitriptan to laboratory animals led to vasoconstriction in the carotid artery. In addition, results from studies in laboratory animals indicate that zolmitriptan blocks central and peripheral trigeminal nerve activity by inhibiting the release of calcitonin gene-related peptide, vasoactive intestinal peptide, and substance P.
In clinical studies, the effect of zolmitriptan on headache and other migraine symptoms (such as nausea, photophobia, phonophobia) was observed after 1 hour and increased from 2 to 4 hours after taking the drug.
Zolmitriptan is equally effective against migraine with aura, migraine without aura, and migraine associated with menstruation. Taking zolmitriptan during an aura did not prevent migraine headaches, so the drug should be taken after the onset of the pain attack.
Indications:
Relief of migraine attacks with or without aura.
Directions for use and dosage:
Apply the film to the surface of the tongue with dry hands.
The recommended dose of the drug to relieve a migraine attack is 2.5 mg (1 film). It is recommended to take the drug as early as possible after the onset of the headache, but the drug is also effective when taken at a later date after the onset of the attack.
If migraine symptoms recur within 24 hours, you can take a second dose of the drug. Do not take a second dose earlier than 2 hours after taking the first dose. If there is no clinical effect after taking the first dose, there is little likelihood of benefit from repeating the drug during the same attack.
If the patient has not achieved a therapeutic effect after taking a dose of 2.5 mg, Zolmsolan can be used at a dose of 5 mg to relieve subsequent migraine attacks.
You should not take more than 2 doses of the drug per day. The total dose of zolmitriptan taken during the day should not exceed 10 mg.
Zolmsolan is not indicated for the prevention of migraine.
Contraindications:
– hypersensitivity to any components of the drug;
– hemiplegic, basilar and ophthalmoplegic migraine;
-uncontrolled arterial hypertension;
-cardiac ischemia;
-coronary vasospasm/Prinzmetal’s angina;
– Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome or arrhythmias associated with other additional impulse pathways;
– diseases of peripheral arteries;
– a history of cerebrovascular accident (including stroke or transient ischemic attack);
-severe renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 15 ml/min);
– combined use with other agonists of serotonin 5HT1B/1D receptors (for example, sumatriptan, naratriptan), ergotamine or its derivatives (including methysergide), as well as within 24 hours after their withdrawal;
– combined use with MAO-A inhibitors and within 14 days after their discontinuation;
– lactose intolerance, lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption;
-pregnancy period (safety of use has not been studied);
-children under 18 years of age;
elderly people over 65 years of age (the effectiveness and safety of use have not been studied).
Precautionary measures:
The drug can only be used in cases of clearly diagnosed migraine. Before prescribing zolmitriptan, as well as other drugs for the relief of migraine, it is necessary to exclude other possible serious neurological diseases in patients with previously undiagnosed migraine, as well as in patients with an established diagnosis of migraine in the presence of atypical symptoms. Zolmitriptan is not indicated for the treatment of hemiplegic, basilar or ophthalmoplegic migraine. Cerebrovascular accidents, including stroke, have been reported in patients taking serotonin 5HT1B/1D receptor agonists. Patients with migraine may be at risk of developing certain cerebrovascular disorders.
Side effects:
From the nervous system: often – sensory disturbances, dizziness, hyperesthesia, paresthesia, drowsiness, sensations of heat or cold, vertigo.
From the cardiovascular system: often – a feeling of palpitations.
From the digestive system: often – abdominal pain; nausea, vomiting, dry mouth.
From the musculoskeletal system: often – muscle weakness, myalgia.
Storage method:
Store at a temperature not exceeding 30 degrees.
Package:
Cardboard box containing